
If the SSM2212 NPN pair is used, it can replace only Q3 and Q4 (output stage) since it contains internal protection diodes across the base and emitter terminals to prevent them from being reverse biased. If you are using just the 2N3904 devices, change the layout as needed.Ĭonstruct the TTL inverter circuit as shown in Figure 5 on your solderless breadboard. The suggested breadboard layouts shown are for the SSM2212 connections. Older kits may contain one SSM2212 matched pair. There are five 2N3904 NPN transistors supplied with the ADALP2000 analog parts kit.
Five small signal NPN transistors (2N3904 and/or SSM2212).The disadvantage is that the logic high voltage is reduced by an amount of the diode drop as shown in Figure 11. Resistor R4 also serves to limit the current that is allowed to flow in the output stage.

This helps prevent potentially large surge currents from flowing in the output stage during transitions between logic states. The diode, D1, serves to increase the effective turn on voltage of Q4, which allows it to be turned off before Q3 turns fully on. Under steady-state conditions, only one transistor is on at a time. Resistor R4 serves to limit the current available from V CC. This output configuration provides the ability to both actively source or sink current and is useful for driving capacitive loads. The output transistor pair, Q3 and Q4 along with diode D1, is referred to as a totem-pole output as shown in Figure 4. This allows Q3 to be on when Q4 is off and vice versa as shown in Figure 3. It allows the input condition to be produced in opposite phases so that the output transistors can be driven in antiphase. The second stage transistor, Q2 in Figure 1, uses a phase splitter to drive both halves of the pull-up and pull-down output stages. The equivalent circuit of the input current steering stage. It provides a higher discharge current to discharge the base when turning it off. The forward current gain or ß F is much larger than the reverse ß R. The transistor is operated in either forward or reverse mode to steer current to or from the second stage transistor’s base, Q2. It can be thought of as a back-to-back diode arrangement. The input stage transistor Q1 performs a current steering function.
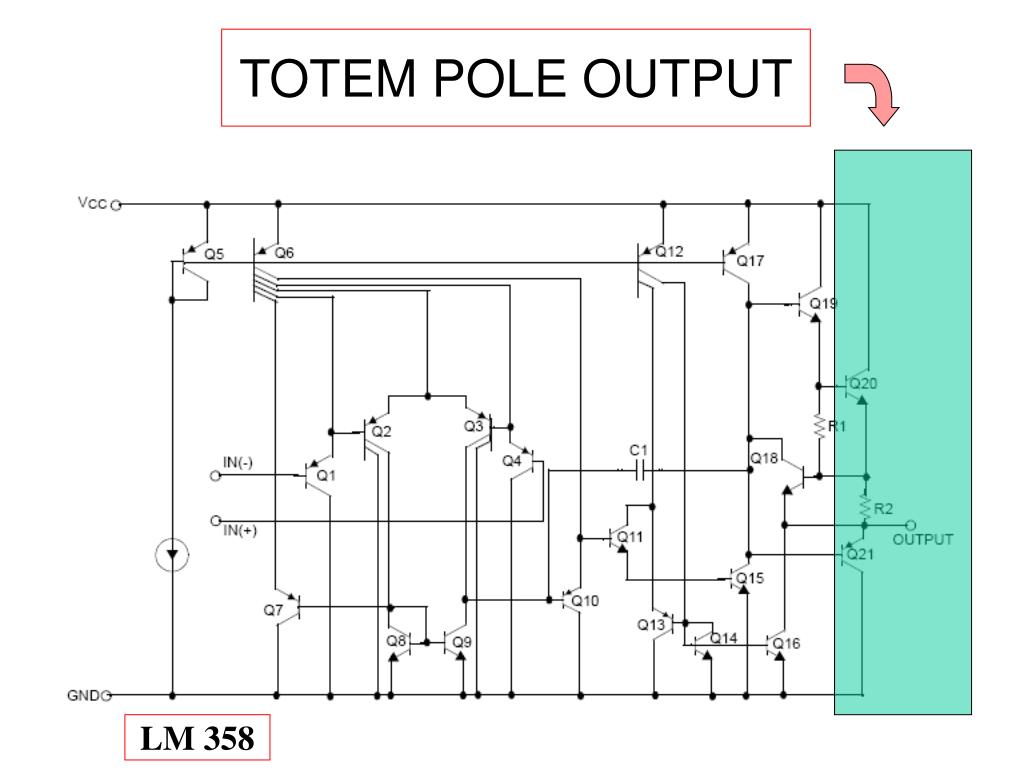
The basic TTL inverter consists of three stages: a current steering input, a phase splitting stage, and an output driver stage. This circuit overcomes the limitations of the single transistor inverter circuit. The schematic of a TTL inverter is shown in Figure 1. In this laboratory activity, the transistor-transistor logic (TTL) circuit inverter (not gate) and 2-input NAND gate configurations are examined. ADALM2000 Activity: TTL Inverter and NAND GateĪ variety of digital logic circuit techniques have been in use since the 1960s when integrated logic gates were first produced.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
